
In this article, we have put together a visual guidebook to better showcase the power of the facial action coding system (FACS). All facial action units are presented with animations to give a first-hand understanding and valuable reference point in the future. So if you are working with facial expression analysis (FEA) we encourage you to bookmark this page – it could just save you a lot of work.
The Facial Action Coding System (FACS) refers to a set of facial muscle movements that correspond to a displayed emotion. Originally created by Carl-Herman Hjortsjö with 23 facial motion units in 1970, it was subsequently developed further by Paul Ekman, and Wallace Friesen. The FACS as we know it today was first published in 1978, but was substantially updated in 2002.
Using FACS, we are able to determine the displayed emotion of a participant. This analysis of facial expressions is one of very few techniques available for assessing emotions in real-time (fEMG is another option). Other measures, such as interviews and psychometric tests, must be completed after a stimulus has been presented. This delay ultimately adds another barrier to measuring how a participant truly feels in direct response to a stimulus.
Researchers have for a long time been limited to manually coding video recordings of participants according to the action units described by the FACS. This process is now possible to complete with automatic facial expression analysis. This saves vast amounts of time and money, as scoring no longer requires analysis of each frame by a trained researcher – the software simply does the work for you.
Below we have listed the major action units that are used to determine emotions. Roll your mouse over the image to start the movement!
Facial coding offers several key benefits in the field of emotion analysis and human behavior research:
| Action Unit | Description | Facial Muscle | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Inner Brow Raiser | Frontalis, pars medialis | |
| 2 | Outer Brow Raiser (unilateral, right side) | Frontalis, pars lateralis | |
| 4 | Brow Lowerer | Depressor Glabellae, Depressor Supercilli, Currugator | |
| 5 | Upper Lid Raiser | Levator palpebrae superioris | |
| 6 | Cheek Raiser | Orbicularis oculi, pars orbitalis | |
| 7 | Lid Tightener | Orbicularis oculi, pars palpebralis | |
| 9 (also shows slight AU4 and AU10) | Nose Wrinkler | Levator labii superioris alaquae nasi | |
| 10 (also shows slight AU25) | Upper Lip Raiser | Levator Labii Superioris, Caput infraorbitalis | |
| 11 | Nasolabial Deepener | Zygomatic Minor | |
| 12 | Lip Corner Puller | Zygomatic Major | |
| 13 | Cheek Puffer | Levator anguli oris (Caninus) | |
| 14 | Dimpler | Buccinator | |
| 15 | Lip Corner Depressor | Depressor anguli oris (Triangularis) | |
| 16 (with AU25) | Lower Lip Depressor | Depressor labii inferioris | |
| 17 | Chin Raiser | Mentalis | |
| 18 (with slight AU22 and AU25) | Lip Puckerer | Incisivii labii superioris and Incisivii labii inferioris | |
| 20 | Lip stretcher | Risorius | |
| 22 (with AU25) | Lip Funneler | Orbicularis oris | |
| 23 | Lip Tightener | Orbicularis oris | |
| 24 | Lip Pressor | Orbicularis oris | |
| 25 | Lips part | Depressor Labii, Relaxation of Mentalis (AU17), Orbicularis Oris | |
| 26 (with AU25) | Jaw Drop | Masetter; Temporal and Internal Pterygoid relaxed | |
| 27 | Mouth Stretch | Pterygoids, Digastric | |
| 28 (with AU26) | Lip Suck | Orbicularis oris | |
| 41 | Lid droop | Relaxation of Levator Palpebrae Superioris | |
| 42 | Slit | Orbicularis oculi | |
| 43 | Eyes Closed | Relaxation of Levator Palpebrae Superioris | |
| 44 | Squint | Orbicularis oculi, pars palpebralis | |
| 45 | Blink | Relaxation of Levator Palpebrae and Contraction of Orbicularis Oculi, Pars Palpebralis. | |
| 46 | Wink | Levator palpebrae superioris; Orbicularis oculi, pars palpebralis |
For Beginners and Intermediates

| Action Unit | Description | Example |
| 51 | Head Turn Left | |
| 52 | Head Turn Right | |
| 53 | Head Up | |
| 54 | Head Down | |
| 55 | Head Tilt Left | |
| 56 | Head Tilt Right | |
| 57 | Head Forward | |
| 58 | Head Back |
Interested in Human Behavior and Psychology?
Sign up to our newsletter to get the latest articles and research send to you
Sign up now
| Action Unit | Description | Example |
| 61 | Eyes Turn Left | |
| 62 | Eyes Turn Right | |
| 63 | Eyes Up | |
| 64 | Eyes Down |
The Action Units described above show the different movements of facial muscles. Certain combined movements of these facial muscles pertain to a displayed emotion. Emotion recognition is completed in iMotions using Affectiva, which uses the collection of certain action units to provide information about which emotion is being displayed. For example, happiness is calculated from the combination of action unit 6 (cheek raiser) and 12 (lip corner puller). A complete list of these combinations and the emotion that they relate to is shown below. The gifs on the right are shown in the same order that the action units listed.
When measuring facial expressions within iMotions, the stimuli are paired automatically to the FACS analysis, allowing you to pinpoint the exact moment that the stimulus triggered a certain emotion. The FACS is also graded on a scale of intensity, which gives a measure of how strongly the emotion is displayed. These measurements can also be synchronized with recordings of galvanic skin response, which provides a measure of arousal. With this information combined, it’s possible to start drawing conclusions about how strongly an individual felt, and what those emotions consisted of, in response to a set stimulus.
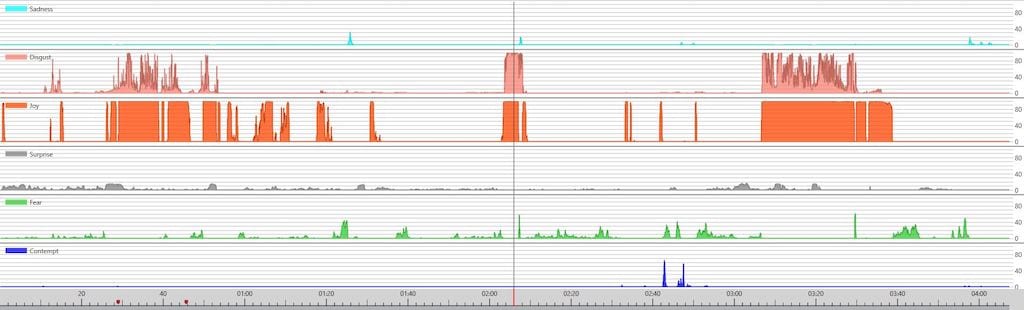
The screenshot below shows how the facial expression data is displayed while a participant watches an advertisement.
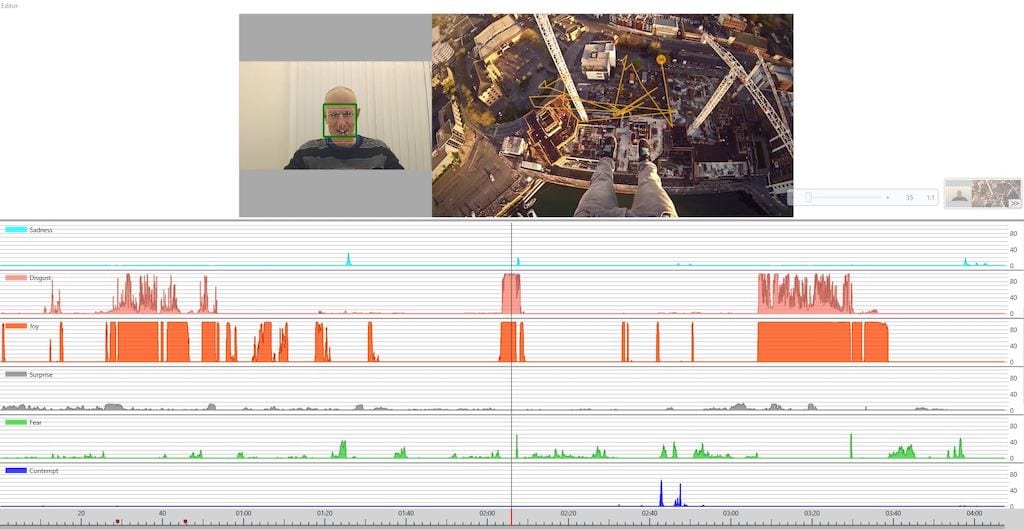
If we zoom in, we can see the intensity of the displayed emotion. There are five emotions displayed in the image below, however iMotions provides a measure of the seven central emotions (shown in the table above), alongside, and in conjunction with measurements of action units.
To choose the best facial action coding software, start by defining your research objectives and budget. Assess essential features like real-time capabilities, interoperability, and ease of use. Research the software’s accuracy, user community, and vendor reputation, and consider trying demo or trial versions when available. Ultimately, select software that aligns with your specific research needs, provides necessary support and training, and fits within your budget constraints.
Integrated into iMotions is the Affectiva Emotion AI, which is a highly specialized emotion recognition technology. The Emotion AI platform is designed for understanding and analyzing human emotions from facial expressions. Here are some key features and details:
Decode emotional expressions as they happen.
The accuracy of the Facial Action Coding System (FACS) is highly dependent on the training and expertise of the individuals using it. When administered by experienced FACS coders under controlled conditions, FACS can achieve a high level of accuracy in coding facial expressions. However, accuracy can vary based on factors like the complexity of emotions and the quality of data collection conditions.
Both yes and no, if you want to become an expert, then training is highly recommended and typically encouraged to use the Facial Action Coding System (FACS) effectively at a high level. If you use software such as Affectiva/iMotions where the software does the coding of the visual stimuli, you typically do not need to be an expert in FACS in order to use it.
Yes, facial coding can be used for real-time emotion recognition in applications such as human-computer interaction, market research, and affective computing. Advances in computer vision and facial recognition technology have enabled the development of real-time facial coding systems that can analyze facial expressions as they occur. These systems use machine learning algorithms to detect and classify emotions based on the movements and patterns of facial muscles in real-time video streams. Real-time emotion recognition through facial coding has applications in areas like user experience design, virtual reality, and customer feedback analysis.
I hope this explanation of action units and FACS has been helpful, and informative. If you’d like to learn even more about facial expressions, then we also have a free pocket guide that you can download for free below!
Keep up with the latest in human behavior research and technological developments
For Beginners and Intermediates

Full-scale human behavior
research solutions
A software research suite that integrates an ecosystem of virtually any biosensor technology to provide the most robust data and insights available.
Trusted by researchers, iMotions Lab lets you collect and analyze data from biosensors and create studies with any stimuli
Webcam Eye Tracking and Facial Expression Analysis for deploying studies quickly and easily around the world, supported by all major browsers